Wholesale Sales Rose 0.7% to $67.5 Billion in February
Apr 28, 2020
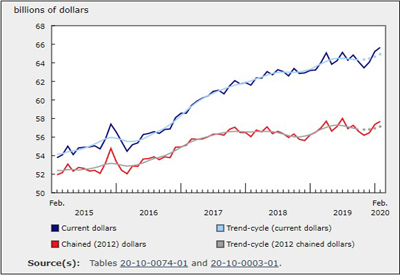
Wholesale sales rose 0.7% to $67.5 billion in February, a third consecutive monthly gain. Three of seven subsectors recorded higher sales, accounting for 51% of total wholesale sales. In dollar terms, the motor vehicle and motor vehicle parts and accessories subsector led the increase. Excluding this subsector, Canadian wholesale sales were down 0.1%.
In volume terms, sales increased 0.6%.
COVID-19 and railway blockades
Respondents were asked to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 and the railway blockades on their sales and inventories for February 2020. All numbers are estimates provided by the respondents, who in many cases could not distinguish between the impact of the pandemic and that of the railway blockades.
Respondents reported that wholesale sales fell by $761 million (unadjusted) due to these disruptions. In the absence of these disruptions, seasonally adjusted wholesale sales would have been estimated to increase by 1.5% in February, instead of the 0.7% rise reported above. In unadjusted dollar terms, at the subsector level, the largest impact was in the machinery, equipment and supplies subsector (-$191 million), led by the computer and communications equipment and supplies industry (-$122 million). The second largest impact was in the food, beverage and tobacco subsector (-$190 million), particularly in the food industry (-$186 million).
The disruptions led to an estimated unadjusted drop in wholesale inventories of $585 million. In dollar terms, the machinery, equipment and supplies subsector (-$154 million) had been affected the most. The second largest impact was in the personal and household goods subsector (-$145 million).
The top two effects of the disruptions as reported by the companies were “disruption in transport” and “”raw material shortage,” which varied by subsector and industry.
One enterprise out of 12 (8.3%) in the wholesale trade sector reported that their activities were affected by COVID-19 only. In terms of the number of enterprises affected, the impact was largest in the food, beverage and tobacco subsector (15.0%) and the personal and household goods subsector (11.4%). Some wholesalers, including companies in the food, the computer, communication and equipment, the motor vehicle, and the personal and household goods industries mentioned that shipments to and from China were adversely affected and caused shortages of raw materials and finished products.
One enterprise out of nine (11.1%) in the wholesale trade sector reported that they were affected only by the railway blockades. In terms of the number of enterprises affected, the impact was largest in the personal and household goods subsector (15.2%) and the building material and supplies subsector (14.7%). Some wholesalers, including companies in the food, the lumber, millwork, hardware and other building supplies and the agriculture supplies industries, mentioned that the railway blockades delayed movements of products to Canadian ports and caused backlogs throughout the supply chain.
Higher sales in February driven by motor vehicle industry
Sales in the motor vehicle and motor vehicle parts and accessories subsector increased 4.2% to $11.9 billion in February. This was the third consecutive monthly gain, following a 2.6% decrease in November 2019. The increase was entirely driven by the motor vehicle industry which saw sales jump 6.5% to a record $9.8 billion. Increases in February of manufactured motor vehicles and exports of passenger cars and light trucks, following extended temporary shutdowns of certain automotive assembly plants in January, contributed to the industry’s strength in wholesale sales in February.
Sales up in five provinces, led by Ontario and Alberta
Five provinces recorded higher sales in February, accounting for 76% of total wholesale sales. Much of the increase was attributable to gains in Ontario and Alberta.
Wholesale sales in Ontario rose 1.2% to $34.6 billion in February, mainly on the strength of gains in the motor vehicle and motor vehicle parts and accessories subsector, which increased 5.4% to $8.5 billion, a third consecutive monthly increase. This subsector gained 12.8% over this three-month span, reaching sales nearly $1 billion greater than those recorded in November 2019.
Sales in Alberta increased 2.3% to $6.7 billion, a second increase in three months. Among the subsectors that recorded higher sales, the machinery, equipment and supplies subsector (+6.9% to $2.1 billion) increased the most; higher sales in this subsector in February followed four consecutive monthly declines.
Wholesale inventories decline
Wholesale inventories declined 0.3% in February to $92.0 billion. Four out of seven subsectors recorded declines, with inventories in the building material and supplies subsector falling most.
Inventories in the building material and supplies subsector dropped 2.5% to $14.5 billion. The decline in February was the subsector’s largest monthly drop since February 2001. Inventories declined in all industries within this subsector, with the lumber, millwork, hardware and other building supplies industry decreasing the most (-3.6% to $6.4 billion).
Inventories fell 0.8% in the motor vehicle and motor vehicle parts and accessories subsector to $13.4 billion due to lower inventories in the motor vehicle (-0.9% to $8.3 billion) and new motor vehicle parts and accessories (-0.6% to $5.1 billion) industries.
Respondents estimated that inventories fell (unadjusted) by $585 million owing to the COVID-19 pandemic and the railway blockades.
The inventory-to-sales ratio continued to decline for a third consecutive month, falling from 1.41 in January to 1.40 in February. The inventory-to-sales ratio is a measure of the time (in months) required to exhaust inventories if sales were to remain at their current level.
Source: Statistics Canada, www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/daily-quotidien/200420/dq200420a-eng.htm?CMP=mstatcan