Integrating High Levels of Renewables into Microgrids: Opportunities, Challenges and Strategies
May 30, 2016
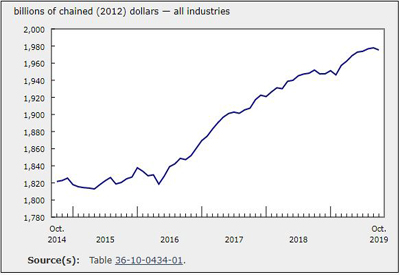
The future of microgrids is bright, and increasingly powered by renewable resources. Over the next five years, forecast GTM Research, overall North American microgrid capacity to more than double. Meanwhile, the annual North American market value is expected to nearly quadruple, increasing from US$225.7 million by the end of 2015 to US$829 million by the end of 2020. Globally, microgrid adoption is also rapidly expanding, with fast-growing Asian markets expected to make up an increasingly larger share of overall deployments.
After going through an analysis of shifts in project economics, microgrid growth, management of high-renewable microgrids and controls, this white paper concludes that microgrids offer tremendous potential to enhance reliability, resilience and long-term energy security, while also decreasing both fossil-fuel dependence and overall energy costs. Global microgrid capacity is forecasted to grow rapidly over the near term, driven by a range of factors that vary among regions and applications. Whether enhancing reliability and resilience, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources, or establishing electricity service where there was none before, microgrids are poised to play a major role going forward.
Project design and equipment selection for high-renewable microgrids in particular can significantly affect system objectives and associated technical challenges. For example, proven technologies and control strategies can compensate for the inherent intermittencies created by renewable generation, providing operators with the flexibility to meet a variety of business, environmental and operational objectives.
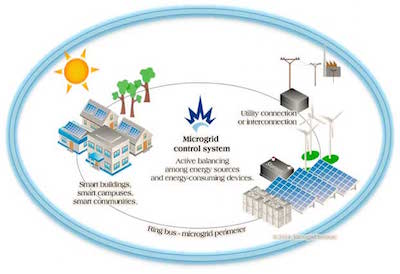
The microgrid market is undergoing a transformation from a niche technology application to a commercially viable modernization tool serving utilities, institutions and remote communities.
As barriers are overcome, high-renewable projects with goals related to reliability, energy cost reductions and grid modernization are expected to be the next growth phase in microgrid development. With the necessary internal system support (frequency stabilization, voltage support, etc.), microgrid operators are able to achieve multiple objectives. These extend beyond behind-the-meter benefits like reliability to include new revenue opportunities from utility and wholesale services.
As microgrid technologies continue to advance and costs decline, business models and regulatory structures are beginning to shift in recognition of the potential benefits these systems offer, both to the end customer and to the utility. Technical challenges remain, but with the right approach and the right tools, microgrid implementations are likely to increase in number and variety in the future.
Adapted from a GTM Research White Paper sponsored by ABB. Read the full document: www.sustainablepowersystems.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/GTM-Whitepaper-Integrating-High-Levels-of-Renewables-into-Microgrids.pdf.